Preparation And Study Of T.S Of Dicot And Monocot Roots And Stems(Primary)
Monocot Stem Cross Section Monocot Root Cross Section Structure (with PPT The main
Overview Test Series Objective The goal is to create a temporary stained mount of a transverse section of dicot and monocot stem and root to investigate various plant tissues. Crack SSC CHSL with India's Super Teachers Get 6 Months SuperCoaching @ just ₹489 ₹449 Your Total Savings ₹40 Purchase Now Want to know more about this Super Coaching ?
NCERT Solutions for Class 11th Ch 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants Biology « Study Rankers
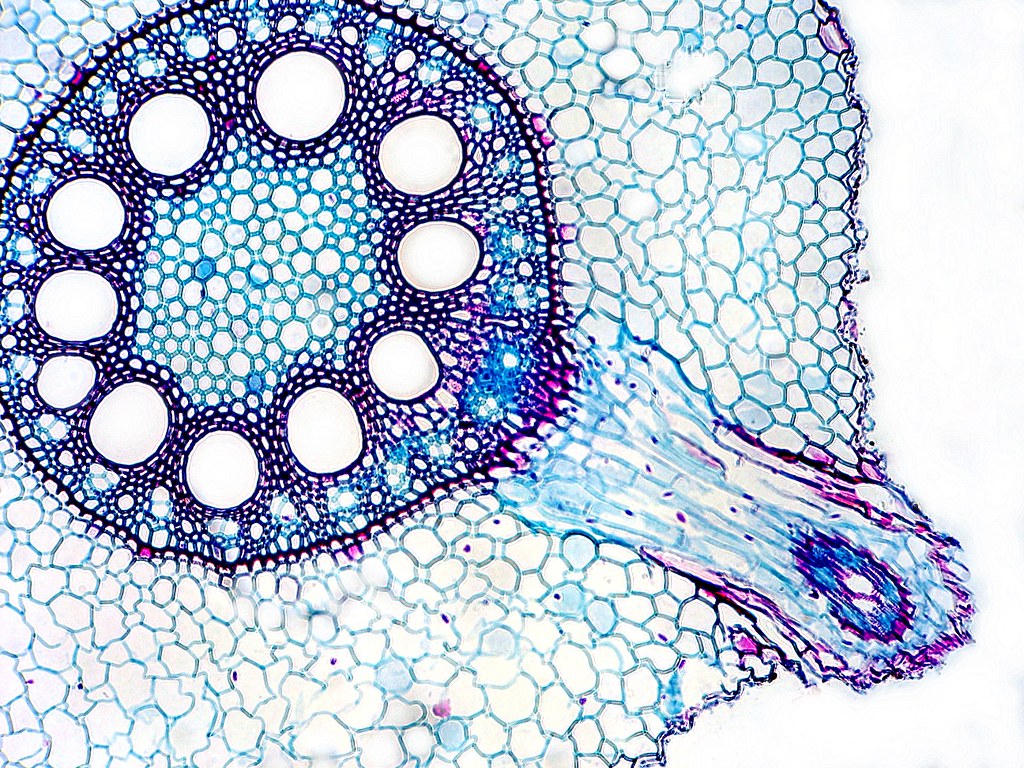
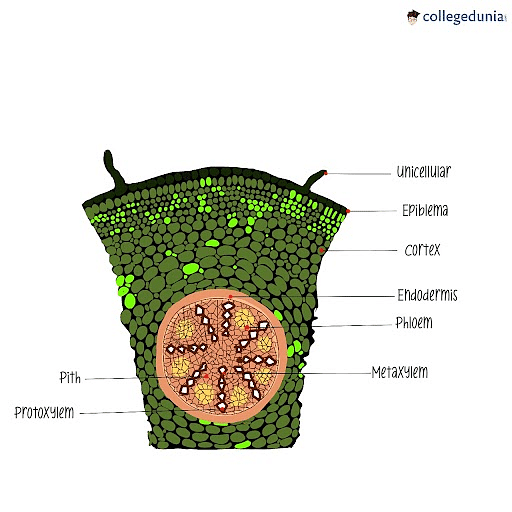
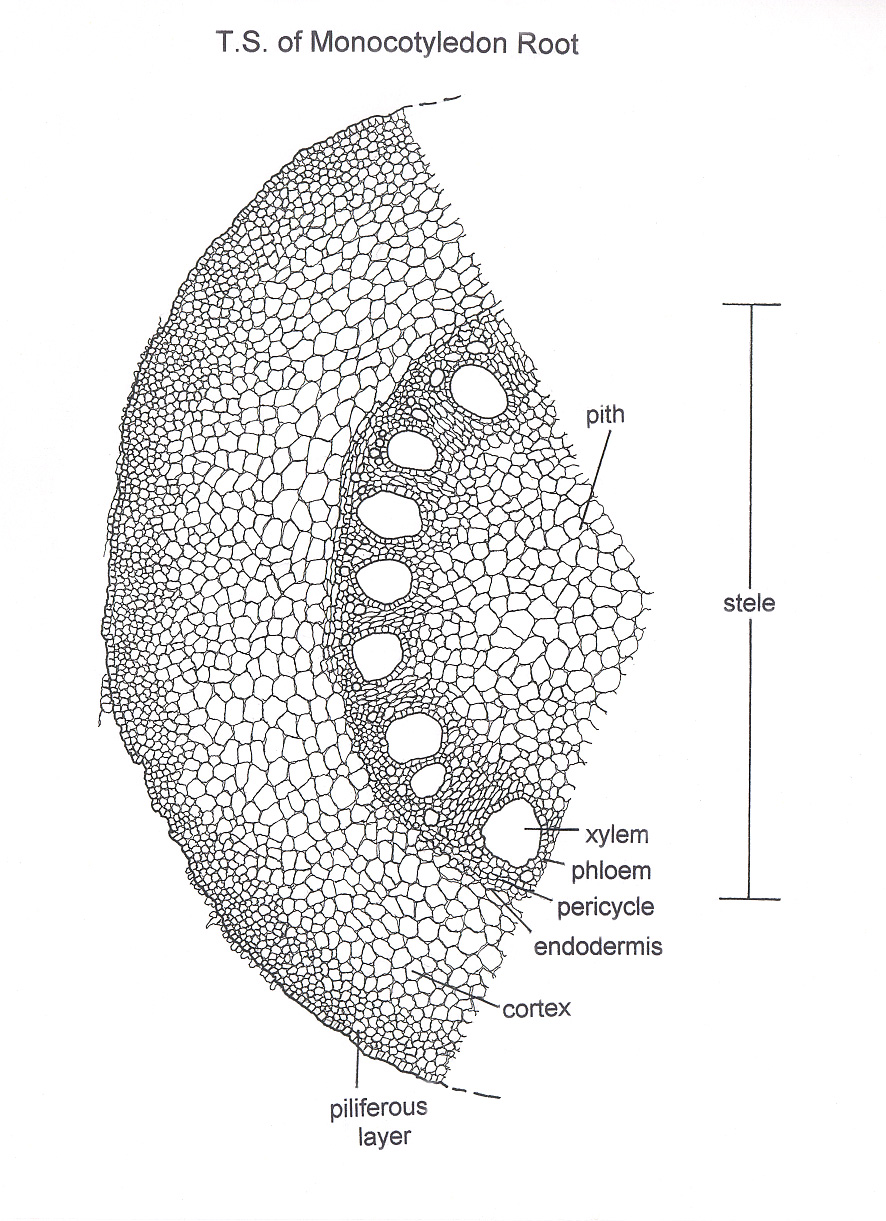
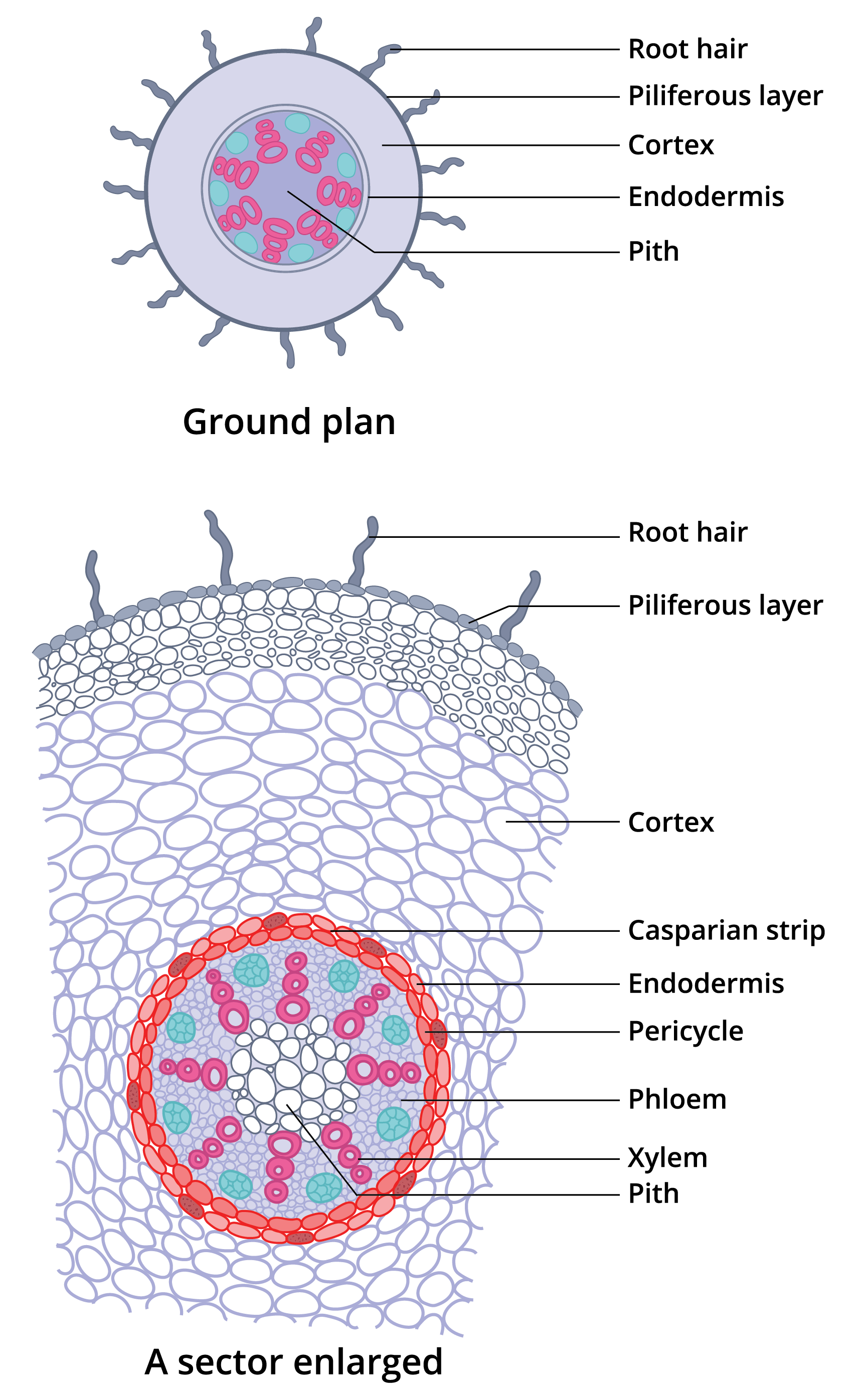
The transverse section of the monocot root (maize) shows the following plan of arrangement of tissues from the periphery to the centre. Piliferous Layer or Epiblema. The outermost layer of the root is known as piliferous layer. It consists of a single row of thin-walled parenchymatous cells without any intercellular space. Epidermal pores and.
Preparation and Study of Transverse Section of Monocot and Dicot Roots and Stems
Monocot Root Anatomy PPT: Anatomy of Monocot Root, Monocot Root Transverse Section Anatomical Details, TS Monocot Root under the Microscope, Record Diagram for Monocot Root, Epidermis, Cortex, Endodermis and Stele of Monocot Roots, Stelar Features of Monocot Roots, Learn more: Notes on Anatomy of Monocot Roots

Transverse section of monocot root Biology diagrams, Root, How to plan
Organ-specific vascular tissue organisation in the monocot rice and the dicot Arabidopsis. (a) Transverse section through a mature rice root. Vascular tissues are organised in a central vascular cylinder surrounded by the endodermis and embedded in the cortex. (b) Transverse section through a mature rice stem internode.
Micscape Image Gallery Botanical Drawing
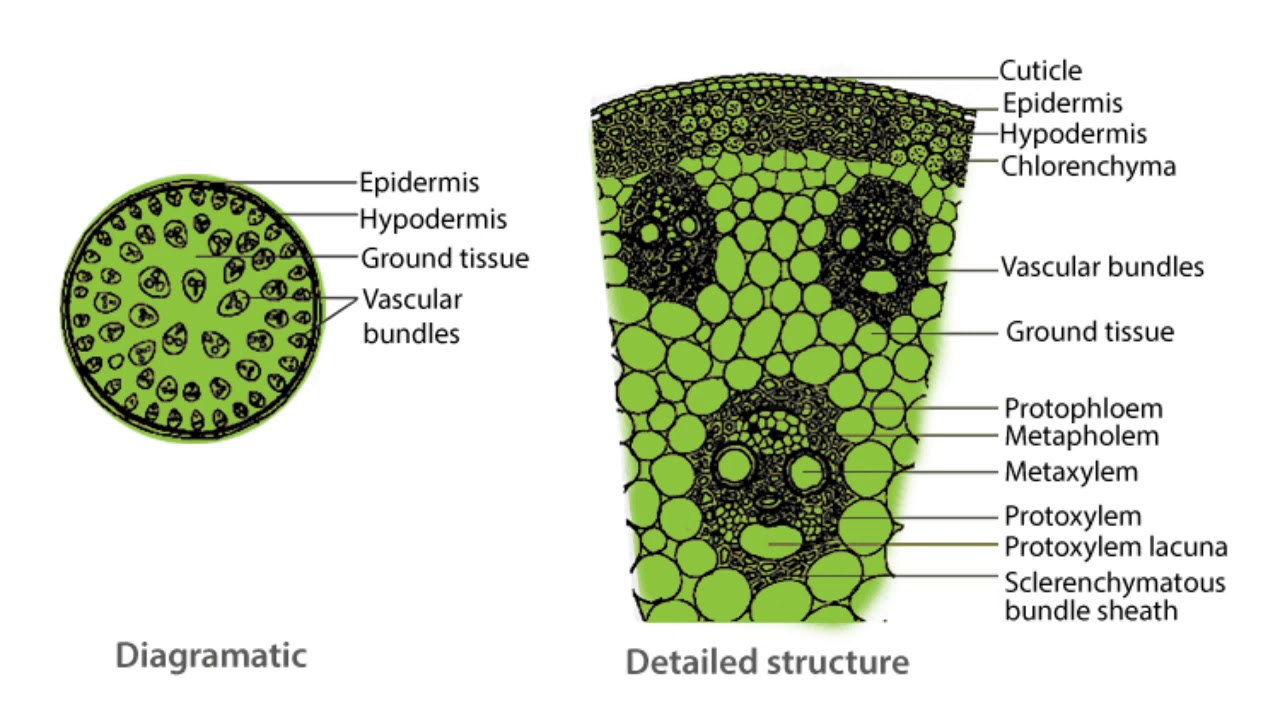
The transverse section of the sunflower root is depicted in the diagram. The following is the internal tissue organization:. In the transverse section of a monocot stem, the epidermis, hypodermis, and ground material are distinguished. The monocot stem's interior tissues are arranged in no particular order.

Chapter 9 Transport in Plants Lesson 1 Monocotyledons and dicot
Article shared by : The secondary growth occurs in herbaceous and woody Lilifloarae (Aloe. Sansevieria, Yucca, Agave, Dracaena) and other groups of monocots. The meristem concerned with this growth is known as cambium. The cambium appears in a direct continuation of a primary thickening meristem.

Primary structure of monocot stem Maize stem Anatomy of monocot stem
1. Epiblema or Piliferous Layer 2. Cortex 3. Endodermis 4. Pericycle 5. Vascular Bundles 6. Conjunctive Tissue 7. Pith Anatomical Characteristics of Dicot Roots ROOT ANATOMY: MONOCOT ROOT CROSS SECTION Monocot Root Diagram Reveals Internal Structure of Monocot Root 1. Epiblema 2. Cortex 3. Endodermis 4. Pericycle

Preparation And Study Of T.S Of Dicot And Monocot Roots And Stems(Primary)
Anatomy of Monocot Root Cross Section The anatomical features of a monocot root can be studied through a cross section (CS) through the root. The present post discesses the anatomy of monocot root with Monocot Root Diagram. Ø Anatomically, the monocot root has been differentiated into the following parts: (1). Epidermis (2). Cortex (3). Endodermis

Transverse section of a part of a typical monocot root has been sho... YouTube
Transverse section of a part of a typical monocot root has been shown in the given figure. Identify the different parts (from \ ( A \) to \ ( E \) ) and select the correct option. (a).

Draw and label the parts of transverse section of monocot root. Brainly.in
Aim: To prepare temporary stained glycerine mounts of transverse sections of stem and root of Dicot and Monocot plants. Material required: Sharp razor, brush, dropper, needles, watch glass, microscopic slides, cover-slips, safrannin, glycerine and compound microscope. Technique: Take 2-3cm long pieces of the material.

Monocot Stem Cross Section
Zea mays. Zea mays (corn) is often used as a model organism for monocot anatomy. Figure 11.1.2.1 11.1.2. 1: The images above show a corn seedling in two different stages of development. The first image is of the corn seedling at an earlier stage. It has produced a shoot (with one cotyledon) and a long root (radicle).
Internal structure of monocot root (Maize) — lesson. Science State Board, Class 10.
A look at monocot and dicot stems. 1. The stem supports the plant, facilitates water and nutrient transport between the different parts of the plant, and contains tissues that help the plant grow. The stem supports the plant, holding up the plant's leaves, flowers, and fruits. Within the stem, bundles of vascular tissue, consisting of xylem.

Monocot Stem Cross Section Monocot Root Cross Section Structure (with PPT The main
How to Draw the Transverse Section of Monocot root | Biology | Grade 11-12https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oOqVXQcyu4sMusic Credits :- https://www.bensound.co.
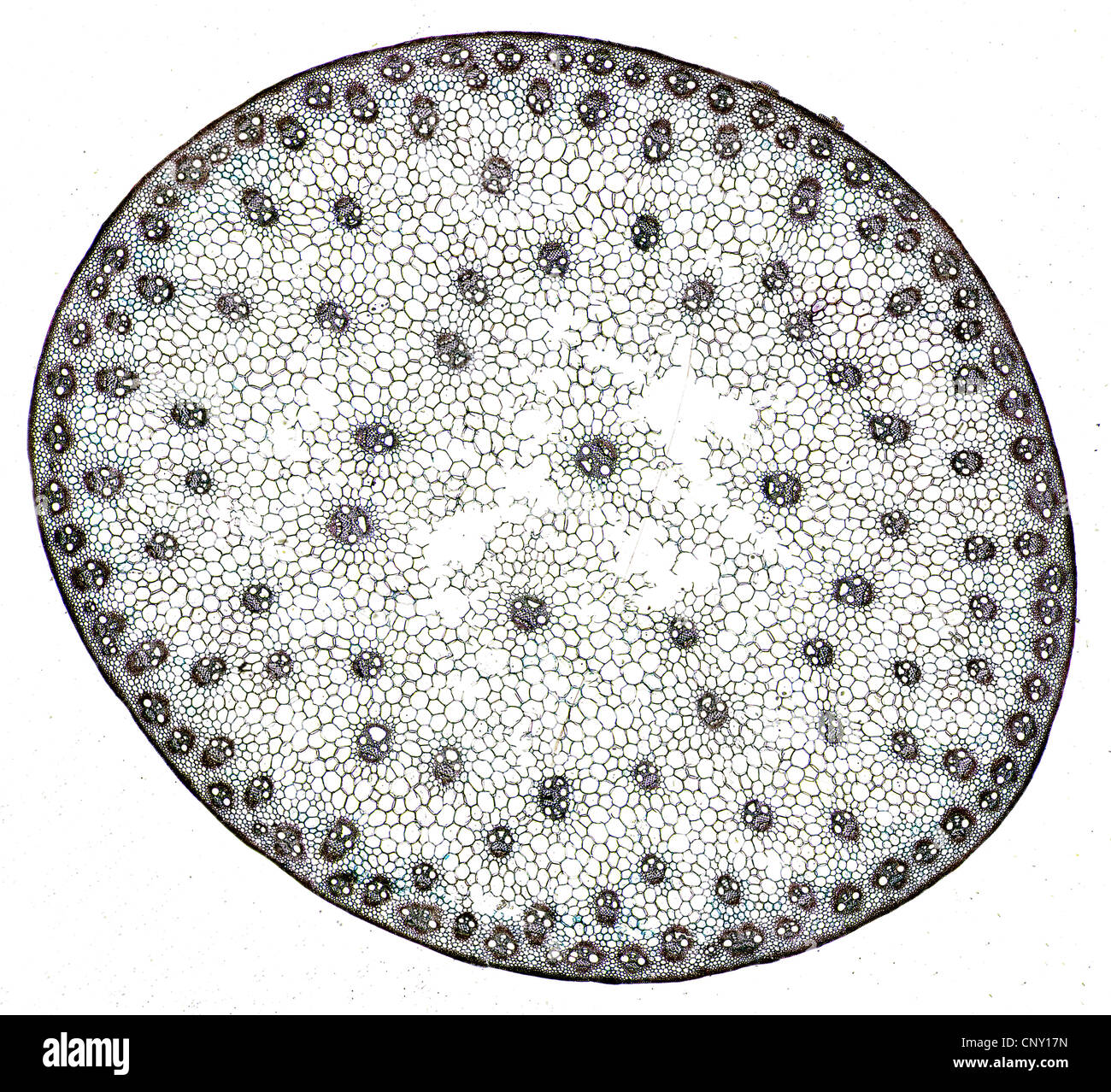
Cross section of a monocot stem with cells and vessel elements Stock Photo, Royalty Free Image
The dicot roots are covered by exodermis which is a modified epidermis. Cortex. The cortex in monocot roots is wide. The cortex in dicot roots is narrow. The cortex in monocot roots is composed of only parenchymatous cells. The cortex of dicot roots is composed of both parenchymatous and sclerenchymatous cells.

Monocot Stem Cross Section
Preparation and Study of the Transverse Section of Dicot and Monocot Roots and Stems Dicot stem Aim The aim of this study is to closely observe the sentient transverse dicot stem. Requirements Some essential materials are required like root as well as stem of a sunflower, fresh root as well as stem of maize, a microscope as well as the blade.
class on structure of monocot stem YouTube
Monocot root In monocot roots, the vascular bundles are arranged in a circular pattern. Monocots and dicots contain two main types of vascular tissue: the xylem and phloem. The xylem carries water and dissolved minerals upward from the roots to the stem and leaves.